There are two types of resources available to HTTPD, static resources and dynamic resources; static resources have our common pictures, JSP, music, audio, etc., and dynamic resources refer to some types of resources that need to be implemented by compiling execution code. They need a MySQL or MariaDB database to assist with the implementation. After running in the background, the results of the operation are returned to the user; after the client sends resources to the server, the server core is accepted and the resource is forwarded to HTTPD for processing. The role of the CGI common gateway interface protocol will direct resources for MySQL processing, and then compile the PHP subprocess according to HTTPD, and then return the result to the client; PHP is the programming language of the common server script;
Configuration of the WordPress blog application in CentOS6.7:
First of all, you need to configure the installation environment of HTTPD, MySQL and PHP;
Install httpd;
In CentOS6.7, the MySQL version must be installed with MySQLD.Server;
And install PHP, and a PHP-MySQL bridge running between PHP and MySQL;
The installation of the above environment exists on a local CD;
Use yum install php httpd php-mysql mysqld.server to install
② For HTTPD configuration, first build a virtual host, build vhosts-www2.conf within /etc/httpd/conf.d//
Just add DocumentRoot and ServerName to the virtual host; you can access the default virtual host of all hosts;
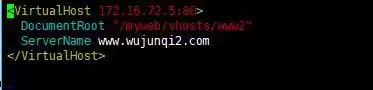
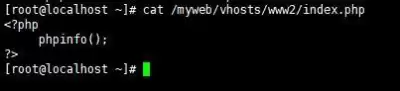
Create the appropriate web files under the document paths to create the file index.php here
Used to detect the connection between PHP and MySQL;
Use httpd -t to detect HTTPD syntax. If there is no error, the next step is to
③ Configure MySQL
Installing a blog system like WordPress requires a database as support, so you need to create a database and create a separate user with any database operation for that database. This requires us to grant this user a WordPress database permission;
First use the MySQL command to enter the MySQL interactive interface
Use the following command
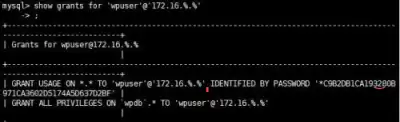
Create a WPDB database
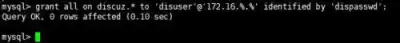
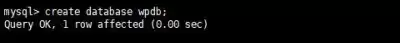 Create a user and give him permissions
Create a user and give him permissions
Use the Show Client command to see if the user's credentials are generated, set the user, the user's password, and access to the IP host segment
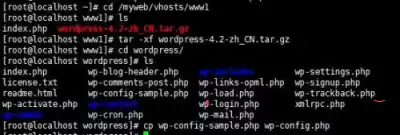
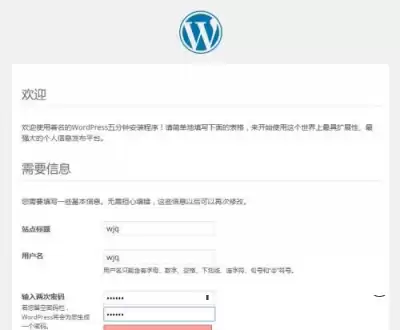
④ Import the WordPress blog program, go down to the Windows environment and use XFTP to transfer the file to the root directory, that is, in the DocumentRoot directory of the previous virtual host; and use the TAR command to decompress; download Version 4.2 Version of WordPress;
There is a file in the WordPress file wp-config-sample.php after decompression.
cp wp-config-sampe.php wp-config.php
And add the WordPress database name, username, user password and IP address of the current host to the copy file;
how:
Use the Mysqld restart service
HTTPD reboot service
At this point, the basic configuration is over and the experiment can be started.;
Add the IP address of the current experimental host in the Windows host file and Mapping ServerName so that you can use ServerName access in the Windows environment;
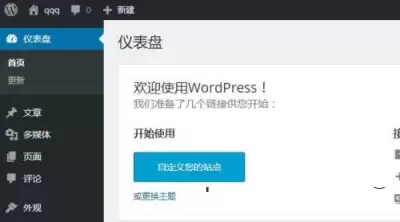
Implementation results:
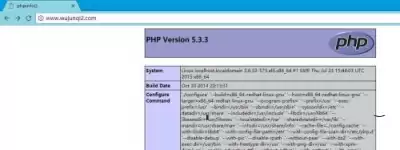
Check the connection between MySQL and PHP
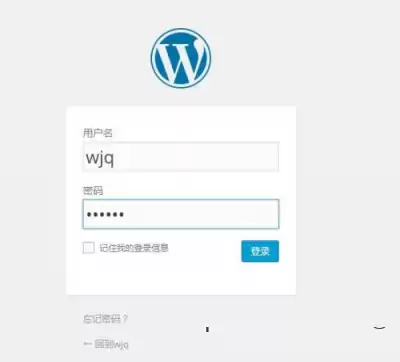
use www.wujunqi2.com/wordpress Interview
Successful login:
Centos7 configure WordPress:
Installation Environment:
The CentOS7 configuration is consistent with CentOS6. The difference is that the MySQL system is MariaDB
You need to install MariaDB.Server;
yum install httpd php mariadb.server php-mysql
In the HTTPD virtual configuration file, you need to set access control for site resources, since access to CentOS7 is not allowed to access;
how:
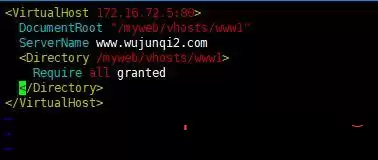
The rest of the configuration is the same as above;
CentOS6 Install Diskoz:
① Install the environment first
yum install php php-mysql mysql-server httpd
② Create an HTTPD virtual host
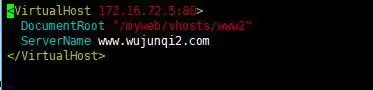
③ Create a database, provide database users for DISCUZ and establish user authority;
![]()
Restarting the service:
service mysqld restart
service httpd restart
④ Download the Discuz application and import it into the root file directory;
Use Unzip to unpack and generate the three file download utility and readme
Use the browser to access
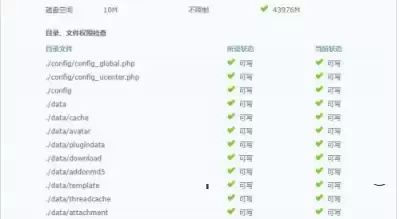
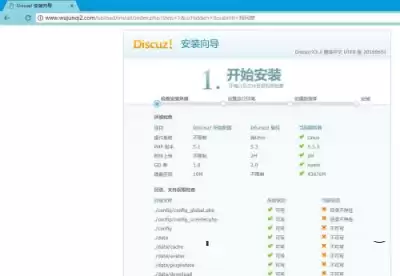 A file that does not exist in the directory requires us to grant 777 permissions:
A file that does not exist in the directory requires us to grant 777 permissions:
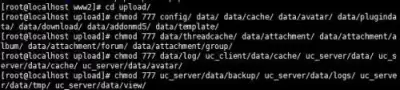 After the power is settled, the page can be labeled:
After the power is settled, the page can be labeled:
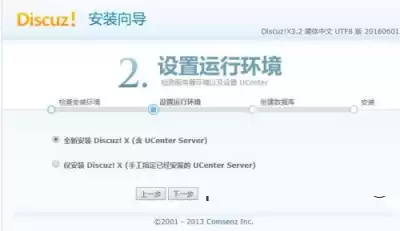
Click next to select a new installation
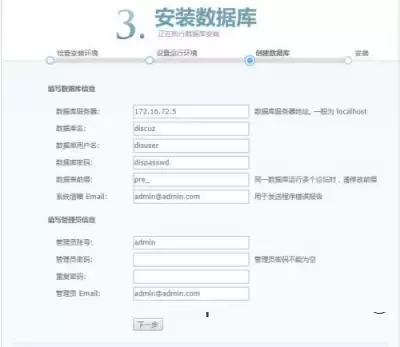
Configure the database, fill in the database created on the command line, and the database user information
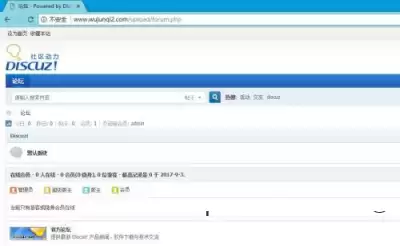
Click on the next step to install the last stage, the installation results are as follows
Configuration of the disk with CentOS7:
The configuration under center7 is about the same as 6, the difference is that
The MySQL version that needs to be installed in the CentOS7 installation environment is MariaDB.Server
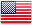
/Etc/httpd/conf.d/vhosts-www1.conf The configuration file must be given an access scope, otherwise it cannot be accessed by default;
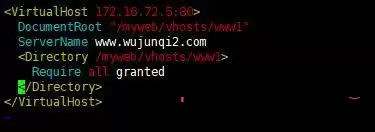
The rest of the configuration operation is usually the same as CentOS6;
 Spain
Spain
 Portugal
Portugal