What is Unicast?
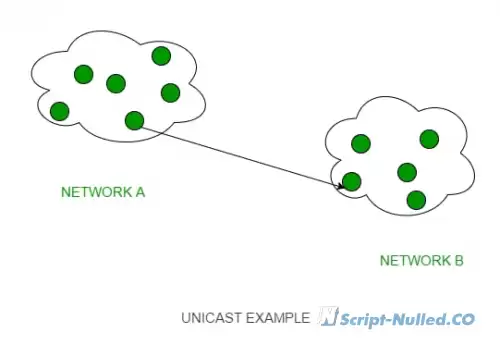
There are 3 main methods of data transmission in IP networks: Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast.
• Unicast – the process of sending a packet from one host to another host. Unicast works in client-server and peer-to-peer networks.
• In unicast packets, the specific IP address of the device for which this packet is intended is used as the destination IP address. The IP address of a particular device consists of a portion of the network address (in which this device is located) and a portion of the host address (a portion that defines this particular stable in its network). This all leads to the possibility of routing unicast packets throughout the network.
• In unicast IP networks, an address is an address, that is, the address of an end device (for example, a computer). For the unicast data transfer type, host addresses are assigned to two end devices and used (these addresses) both the source IP address and the destination IP address.
 Spain
Spain
 Portugal
Portugal




