Evilginx2: Phishing and 2FA Bypass
In this article, we will talk about phishing and bypassing two-factor authentication using a wonderful tool – Evilginx2.
The second version of Evilginx attracts with its feature to help penetration testers, and other good people bypass two-factor authentication, and receive credentials from various accounts of the target.
Evilginx2 is a "man-in-the-middle" type framework used for phishing login credentials along with session cookies, which, in turn, allows you to bypass the protection of two-factor authentication.
This tool is the successor to Evilginx, released in 2017, which used a custom version of the nginx HTTP server to provide "man-in-the-middle" functionality as a proxy between the browser and a phishing website. The current version is written entirely in GO, as a separate application.
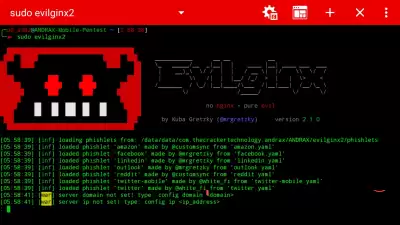
Evilginx2 - implements its own HTTP and DNS server, which makes it extremely easy to configure and use.
As an attacking system, I use Kali Linux Full Upgrade, and since Evilginx2 is written in GO, we install the latest version of it for ourselves:
Calling Help:
Code:
evilginx2 –h
In addition to this, there is an internal help for commands in Evilginx2 itself.
We proceed to setting up the tool before carrying out the attack.
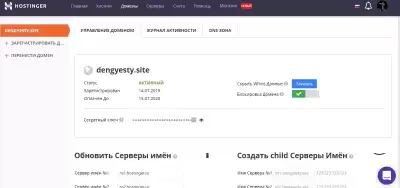
We register the domain and configure the name servers (ns1 and ns2) in the admin panel of the domain provider so that they point to the IP address of your server with Evilginx.
Configure the domain and IP address of your server using the following commands:
Code:
config domain yourdomain.com
config ip (your ip)
Now you can configure the phishlet you want to use. In this case, it will be Twitter's phishlet. Set the hostname for phishlet (it should contain your domain).
Code:
phishlets hostname twitter twitter.com.maligncorp.com
Then you need to get CNAME's for the twitter phishlet, and register them in the Domain provider admin panel:
A canonical name (CNAME record) is a type of DNS record that binds an alias to a valid (canonical) domain name. CNAME records are usually used to bind a subdomain, such as www or mail, to the domain where the content of this subdomain is hosted. For example, a CNAME record can bind a web address www.example.com to the actual website for the domain example.com .
Code:
phishlets get-hosts twitter
Adding these names to the control panel:
We include a fishlet in the work:
Code:
phishlets enable twitter
We are waiting for certificates to be received, and if everything went well, we see this conclusion.
With this – everything is OK, it turned out. Now two-factor authentication, a little help:
Two-factor authentication is a method of identifying a user in a service (usually on the Internet) by requesting authentication data of two different types, which provides two-layer, and therefore more effective protection of the account from unauthorized intrusion. In practice, it usually looks like this: the first milestone is a login and password, the second is a special code that comes by SMS or email. Less often, the second "layer" of protection requests a special USB key or biometric data of the user. In general, the essence of the approach is very simple: to get somewhere, you need to confirm twice the fact that you are you, and with the help of two "keys", one of which you own, and the other you keep in memory.
Consider a situation when, for example, you need to restore the password, the same DFA using the phone.
An SMS comes from the service, and we enter the received code:
The victim resets the password, in this case we don't get it, our profit is the cookie of the current session:
We look at what we have in the session and copy the data to import into the browser:
The result is quite predictable:
That's all I wanted to tell you. Evilginx2 is a very cool tool, I advise you to look at the contents of the /phislets folder, I'm sure it will prompt certain thoughts.
 Spain
Spain
 Portugal
Portugal